What is Mastoiditis?
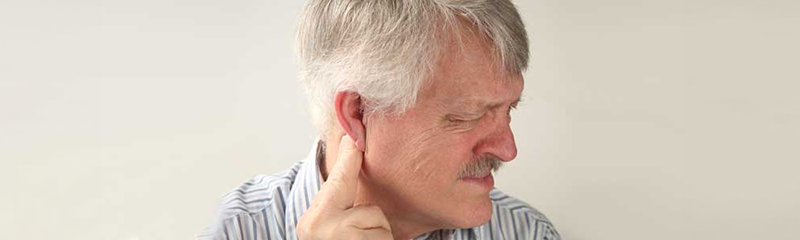
Mastoiditis occurs when a serious ear infection spreads to the mastoid bone located behind the middle ear. When determining what is mastoiditis, the infection is characterized by trapped fluid in the air space in the middle ear resulting in noticeable swelling and inflammation behind the ear. Those with weakened or compromised immune systems are at higher risk of mastoiditis. As a result, once you have discovered what is mastoiditis, it will be most commonly seen in children and infants. If not dealt with quickly with antibiotics, serious complications can occur, and surgery may be necessary.
Best Mastoiditis Medication
What is mastoiditis and its symptoms can manifest as localized swelling behind the ear and excessive redness in patches around the area. The ear may start to protrude due to swelling. Clear or pus-filled discharge will also start leaking from the infected ear. If some or all these symptoms start appearing, as well as those from a flu or fever, seek medication attention as soon as possible. Start treatment immediately as directed by your doctor.
So, what can cause pain on your mastoid bone? If antibiotics are not taken right away the infection can develop into an antibiotic-resistant infection. In fact, mastoiditis is usually caused by an untreated middle ear infection which has spread to the inner ear. Once the infection has spread to the area, the mastoid bone starts to disintegrate causing it to become infected as well. During a cold or the flu, bacteria can travel and infect different parts of the ear as well as create growths called cholesteatomas which can block the ear and lead to what is mastoiditis. When blockage occurs, bacteria gets trapped in the ear and multiplies, causing the mastoiditis.
Mastoiditis Symptoms and Treatment
When assessing what is mastoiditis, symptoms can present themselves 2-6 days after an ear infection has occurred, even if that initial infection has already cleared up. The patient will start to feel tenderness and swelling behind the ear. Symptoms are similar to those from an ear infection and may appear as if the ear infection is getting worse. When new symptoms occur days or weeks after the first ear infection, your doctor will determine if the cause was from the nature of what mastoiditis is. Common symptoms include:
Fever
Irritability
Fatigue or lethargy
Ear discharge
Ear pain
Headache
Vomiting or loss of appetite
Severe mastoiditis may result in serious health complications such as a brain abscess or other infections. If your mastoiditis creates a high fever or excessive swelling around your head, seek medical attention immediately. If left untreated, mastoiditis can lead to the following health problems:
Vertigo, nausea or dizziness
Facial paralysis
Hearing loss
Changes in vision
Meningitis
Epidural abscess
Sepsis
These serious complications are rare for most people, but despite treatment, infections and symptoms may still reoccur, especially for those with weak or compromised immune systems. Your doctor will diagnose what mastoiditis is by imaging the mastoid area and collecting samples. Checking your white blood cell count is also a good indication for a doctor to determine if you have an infection. Once mastoiditis is detected, the doctor may perform a spinal tap to see if the infection has spread to the spinal column. Before starting any treatment, get a full assessment and review of your medical history from your doctor.
Mastoiditis Treatment
Early detection and treatment with antibiotics are vital to avoid complications. Once diagnosed, your doctor will prescribe a round of oral antibiotics such as Ciprofloxacin, as well as specialized eardrops. If you visit the hospital, they will administer antibiotics intravenously to stop the infection from spreading. For a serious case of mastoiditis, surgery may be necessary if antibiotics are unsuccessful at treating the infection. Doctors can either drain the infected fluid from the ear or perform a mastoidectomy to remove the infected part of the mastoid bone.
Once treatment is complete, an ear, nose, and throat specialist should verify if the infection is gone and under control. Treating the initial ear infections right away is the best way to prevent future cases of mastoiditis. If you do find yourself suffering from a cold or flu, being extra vigilant towards germs by washing your hands more, will reduce the risk of an ear infection from occurring. When you are sick, refrain from smoking or getting into contact with secondhand smoke to avoid aggravating your infection. If you are taking antibiotics for an ear infection, please ensure you take the entire round of medication, because despite feeling better, remaining bacteria may still spread and cause mastoiditis.
Contact your doctor immediately if you suspect you may have mastoiditis. A severe case of mastoiditis can become life-threatening if not treated immediately. Once a person has severe ear infection symptoms, they should see a doctor within 24-48 hours. To learn more about what is mastoiditis, visit our blog to discover more helpful health advice and treatment suggestions.
References:
Chronic Otitis Media, Cholesteatoma and Mastoiditis – Harvard Health Publishing – Harvard Medical School
IMPORTANT NOTE: The above information is intended to increase awareness of health information and does not suggest treatment or diagnosis. This information is not a substitute for individual medical attention and should not be construed to indicate that use of the drug is safe, appropriate, or effective for you. See your health care professional for medical advice and treatment.